Set Operator: Distinct
The following table lists all Set operators available in LINQ.
| Set Operators | Usage |
|---|---|
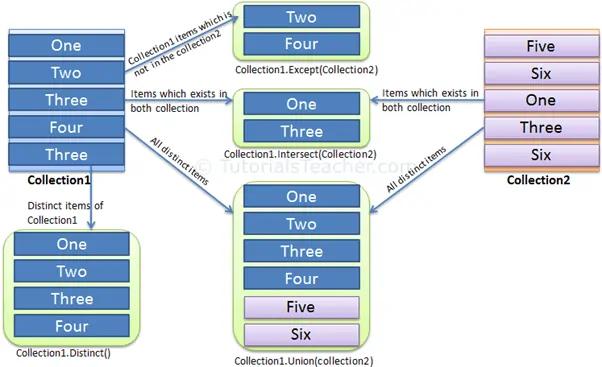
| Distinct | Returns distinct values from a collection. |
| Except | Returns the difference between two sequences, which means the elements of one collection that do not appear in the second collection. |
| Intersect | Returns the intersection of two sequences, which means elements that appear in both the collections. |
| Union | Returns unique elements from two sequences, which means unique elements that appear in either of the two sequences. |
The following figure shows how each set operators works on the collections:
Distinct
The Distinct extension method returns a new collection of unique elements from the given collection.
IList<string> strList = new List<string>(){ "One", "Two", "Three", "Two", "Three" };
IList<int> intList = new List<int>(){ 1, 2, 3, 2, 4, 4, 3, 5 };
var distinctList1 = strList.Distinct();
foreach(var str in distinctList1)
Console.WriteLine(str);
var distinctList2 = intList.Distinct();
foreach(var i in distinctList2)
Console.WriteLine(i);Two
Three
1
2
3
4
5
The Distinct extension method doesn't compare values of complex type objects. You need to implement IEqualityComparer<T> interface in order to compare the values of complex types. In the following example, StudentComparer class implements IEqualityComparer<Student> to compare Student objects.
public class Student
{
public int StudentID { get; set; }
public string StudentName { get; set; }
public int Age { get; set; }
}
class StudentComparer : IEqualityComparer<Student>
{
public bool Equals(Student x, Student y)
{
if (x.StudentID == y.StudentID
&& x.StudentName.ToLower() == y.StudentName.ToLower())
return true;
return false;
}
public int GetHashCode(Student obj)
{
return obj.StudentID.GetHashCode();
}
}Now, you can pass an object of the above StudentComparer class in the Distinct() method as a parameter to compare the Student objects as shown below.
IList<Student> studentList = new List<Student>() {
new Student() { StudentID = 1, StudentName = "John", Age = 18 } ,
new Student() { StudentID = 2, StudentName = "Steve", Age = 15 } ,
new Student() { StudentID = 3, StudentName = "Bill", Age = 25 } ,
new Student() { StudentID = 3, StudentName = "Bill", Age = 25 } ,
new Student() { StudentID = 3, StudentName = "Bill", Age = 25 } ,
new Student() { StudentID = 3, StudentName = "Bill", Age = 25 } ,
new Student() { StudentID = 5, StudentName = "Ron" , Age = 19 }
};
var distinctStudents = studentList.Distinct(new StudentComparer());
foreach(Student std in distinctStudents)
Console.WriteLine(std.StudentName);Steve
Bill
Ron
Distinct operator in Query Syntax
The Distinct operator is Not Supported in C# Query syntax. However, you can use Distinct method of query variable or wrap whole query into brackets and then call Distinct().
Use the Distinct keyword in VB.Net query syntax:
Dim strList = New List(Of string) From {"One", "Three", "Two", "Two", "One" }
Dim distinctStr = From s In strList _
Select s Distinct