Python Module Attributes: name, doc, file, dict
Python module has its attributes that describes it. Attributes perform some tasks or contain some information about the module. Some of the important attributes are explained below:
__name__ Attribute
The __name__ attribute returns the name of the module. By default, the name of the file (excluding the extension .py) is the value of __name__attribute.
import math
print(math.__name__) #'math'In the same way, it gives the name of your custom module e.g. calc module will return 'calc'.
import calc
print(calc.__name__) #'calc'However, this can be modified by assigning different strings to this attribute. Change hello.py as shown below.
def SayHello(name):
print ("Hi {}! How are you?".format(name))
__name__="SayHello"And check the __name__ attribute now.
import hello
print(hello.__name__) #'SayHello'The value of the __name__ attribute is __main__ on the Python interactive shell and in the main.py module.
print(__name__)When we run any Python script (i.e. a module), its __name__ attribute is also set to __main__. For example, create the following welcome.py in IDLE.
print("__name__ = ", __name__)Run the above welcome.py in IDLE by pressing F5. You will see the following result.
__name__ = __main__
However, when this module is imported, its __name__ is set to its filename. Now, import the welcome module in the new file test.py with the following content.
import welcome
print("__name__ = ", __name__)Now run the test.py in IDLE by pressing F5. The __name__ attribute is now "welcome".
__name__ = welcomeThis attribute allows a Python script to be used as an executable or as a module.
Visit __main__ in Python for more information.
__doc__ Attribute
The __doc__ attribute denotes the documentation string (docstring) line written in a module code.
import math
print(math.__doc__)Consider the the following script is saved as greet.py module.
"""This is docstring of test module"""
def SayHello(name):
print ("Hi {}! How are you?".format(name))
returnThe __doc__ attribute will return a string defined at the beginning of the module code.
import greet
print(greet.__doc__)__file__ Attribute
__file__ is an optional attribute which holds the name and path of the module file from which it is loaded.
import io
print(io.__file__) #output: 'C:\python37\lib\io.py'__dict__ Attribute
The __dict__ attribute will return a dictionary object of module attributes, functions and other definitions and their respective values.
import math
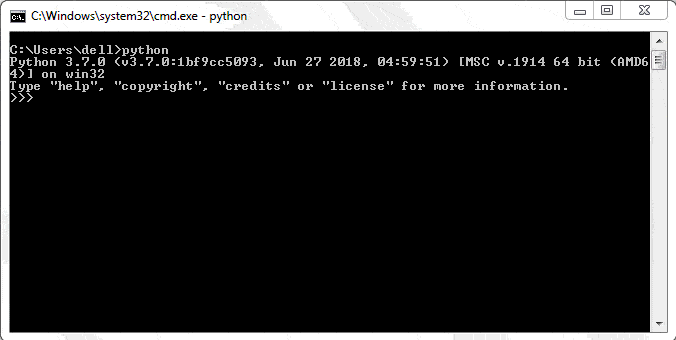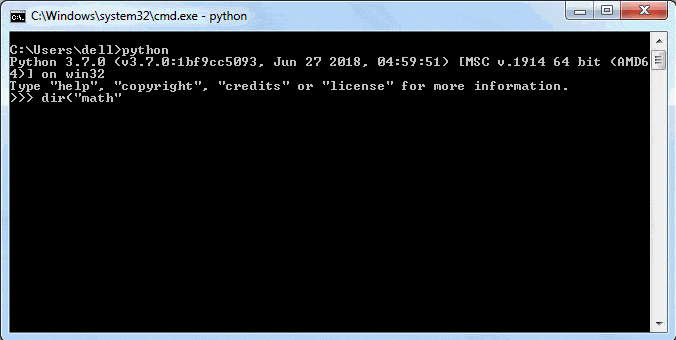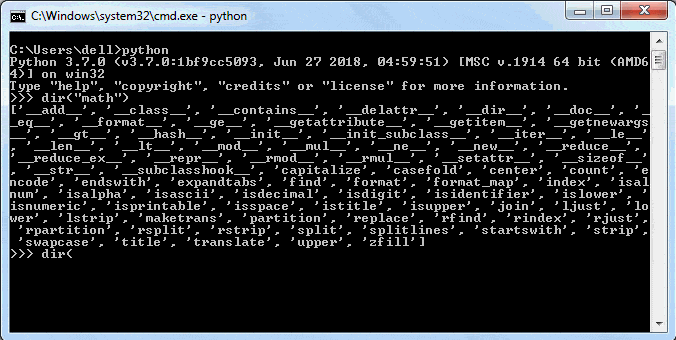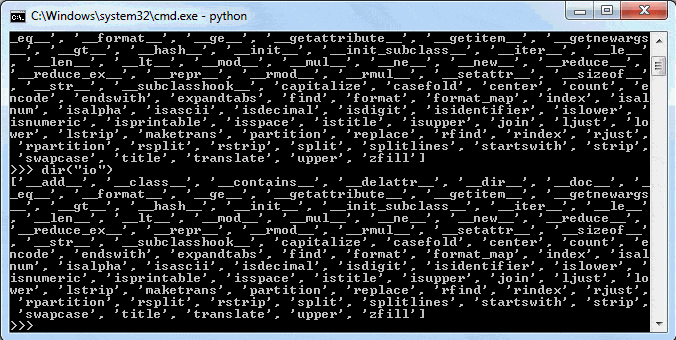
print(math.__dict__)The dir() is a built-in function that also returns the list of all attributes and functions in a module.
import math
print(dir("math"))You can use the dir() function in IDLE too, as shown below.
Learn more about module attributes in Python Docs.
