PostgreSQL SELECT Statement
Postgres support the SELECT statement to retrieve records from the zero or more tables or views in the database.
SELECT [ * | column1, column2,... | expression ]
[ FROM [table1 [, table2,..] [,view1, view2..]
[ WHERE condition ]
[ GROUP BY [ column1 [,column2,..]]]
[ HAVING condition ]
[ WINDOW window_name AS ( window_definition )]
[ ORDER BY expression [ ASC | DESC | USING operator ] ]
[ LIMIT { count | ALL } ]
[ OFFSET start [ ROW | ROWS ] ]
[ FETCH { FIRST | NEXT } [ count ] { ROW | ROWS } { ONLY | WITH TIES } ]
[ FOR { UPDATE | NO KEY UPDATE | SHARE | KEY SHARE } [ OF table_name] [ NOWAIT | SKIP LOCKED ]]With the SELECT statement,
- Specify one or more column names after the SELECT clause for which you want to retrieve the data. Multiple column names should be separated by a comma.
- Optionally specify expression also with the SELECT clause.
- Specify asterisk(*) after SELECT to select all the columns. The select list can also contain expressions or literal values.
- Specify one or more table names from which you want to select data after the FROM clause.
- Optionally, use WHERE, GROUP BY, HAVING, ORDER BY, WINDOW, LIMIT, OFFSET, FETCH, FOR clause.
SQL keywords are case-insensitive, so you can write SELECT, Select, or select. For formatting purposes, we will keep all SQL keywords in capital letters.
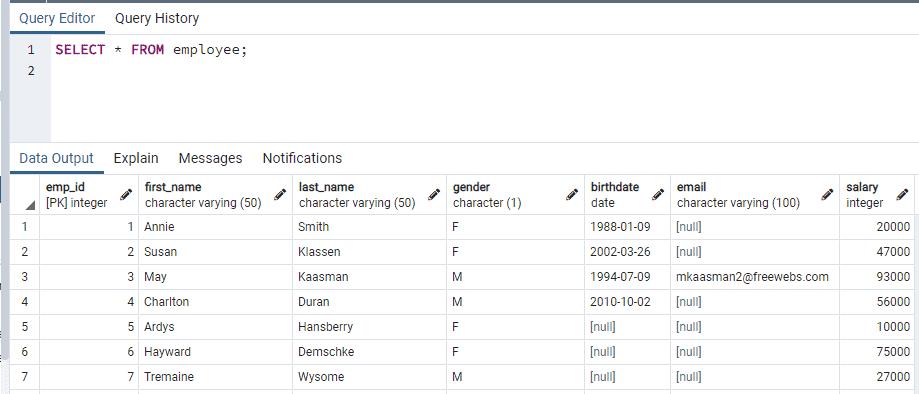
Let's see how to use the SELECT statement to fetch the data from the following employee table.
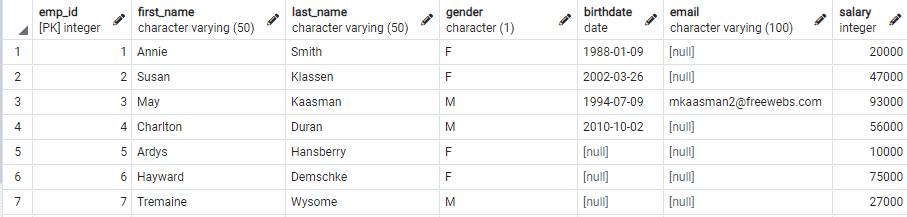
The following SELECT statement retrieves the data from the single column of the employee table.
SELECT first_name FROM employee;The following shows the result in pgAdmin.
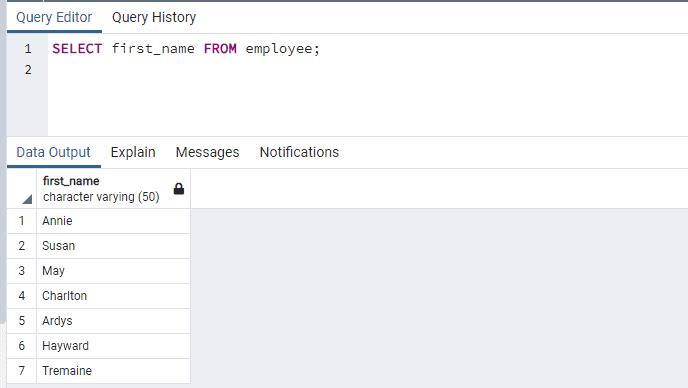
The following SELECT statement retrieves the data from multiple columns of the employee table.
SELECT emp_id, first_name, last_name FROM employee;The following shows the result in pgAdmin.
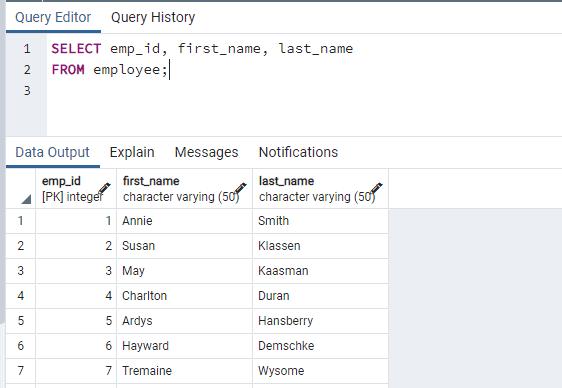
The following SELECT statement uses * to retrieve the data from all columns of the employee table.
SELECT * FROM employee;The following shows the result in pgAdmin.
Expression with SELECT Clause
You can use the expression in the SELECT statement. The following concatenates first_name and last_name columns using the || operator.
SELECT first_name || ' ' || last_name FROM employee;The following shows the result in pgAdmin.
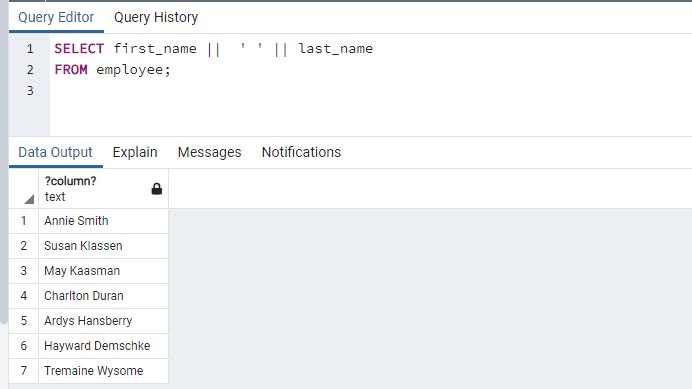
It can also return the result of the basic math operation.
SELECT 6 * 4;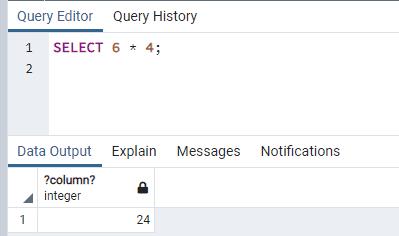
Column Alias
An alias lets you assign a temporary name to a column or expression in the SELECT statement. Alias makes a column more readable in the result set of the SELECT query. Column alias exists only for the duration of the query.
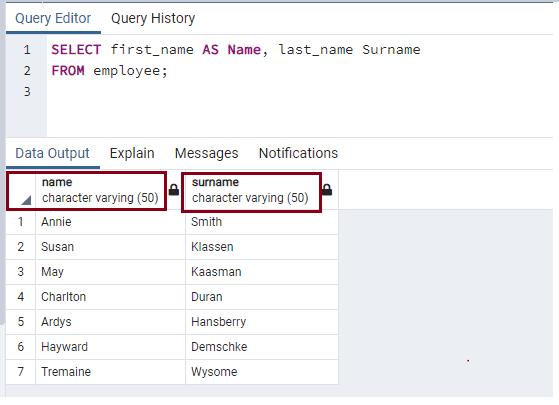
The following query renames the first_name column to Name and last_name to Surname in the result.
SELECT first_name AS Name, last_name Surname FROM employee;The following shows the result in pgAdmin.
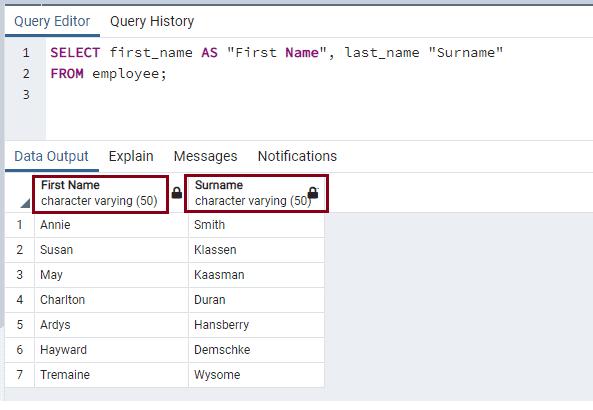
Use double-quotes (") to include space or change the case of the column alias name, as shown below.
SELECT first_name AS "First Name", last_name "Surname"
FROM employee;The following shows the result in pgAdmin.
Thus, you can use the SELECT statement to retrieve data from the table. You will learn how to retrieve data from multiple tables in the join section.
