PostgreSQL Serial Type
In PostgreSQL, a database table can be created by defining column datatype as SERIAL. It is used to define a column of the table as an auto-increment column.
CREATE TABLE <table_name> (
<column_name> SERIAL
);When you assign a SERIAL data type to any column, PostgreSQL will perform following
- Create a sequence object and assign the next value generated by the sequence as a default value to a column. The default name of sequence would be
<table_name>_<column_name>_seq. - Add NOT NULL constraint to the SERIAL type column of the table. The sequence will always generate an integer value and assign it to the column whenever data is inserted into the table, hence column will always be NOT NULL.
- The column will be the owner of the sequence. If the column is dropped or the table is deleted, the sequence will be automatically dropped.
| Name | Storage | Byte range |
|---|---|---|
| SMALLSERIAL | 2 bytes | 1 to 32,767 |
| SERIAL | 4 bytes | 1 to 2,147,483,647 |
| BIGSERIAL | 8 bytes | 1 to 9,223,372,036,854,775,807 |
Let's create the CARS table with a primary key column of SERIAL type.
CREATE TABLE CARS(
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
brand VARCHAR NOT NULL
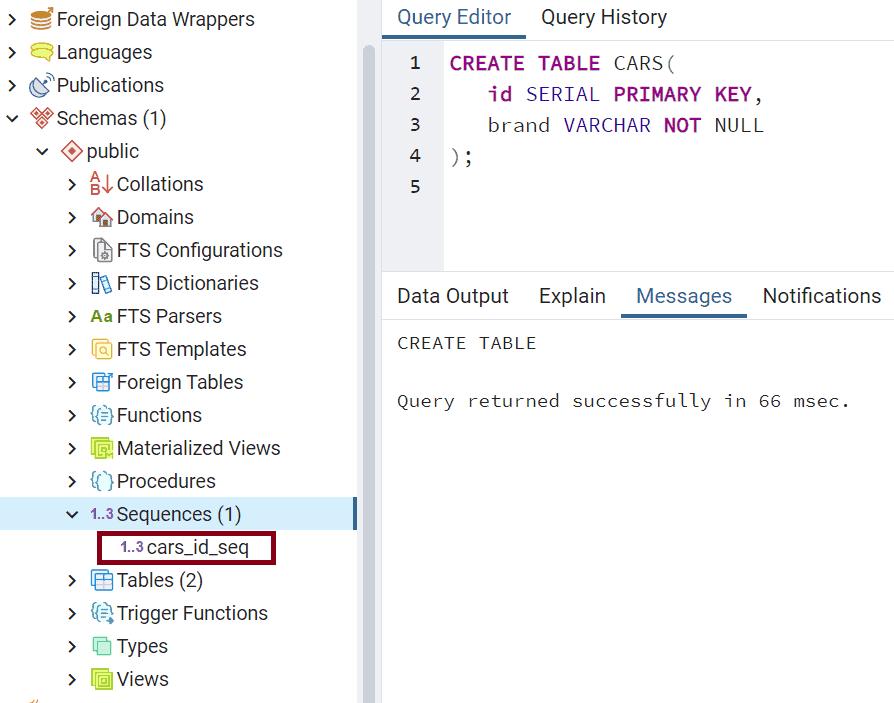
);When you execute the above statement, it will create index cars_id_seq as bellow
Now let's try to insert data into the CARS table and see how the values of the id column are inserted. To assign sequence generated value to the id column of the CARS table when you insert a row into the table, either you ignore that column or use the DEFAULT keyword for that column, as shown below.
INSERT INTO CARS(brand)
VALUES('Fiat');
INSERT INTO CARS(id, brand)
VALUES(DEFAULT, 'Honda');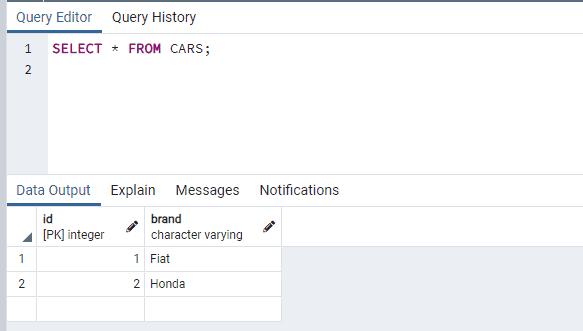
As you can see, two rows were inserted into the table with the id column populated as 1 and 2.
You can check the current value of the sequence using the sequence manipulation function currval() function.
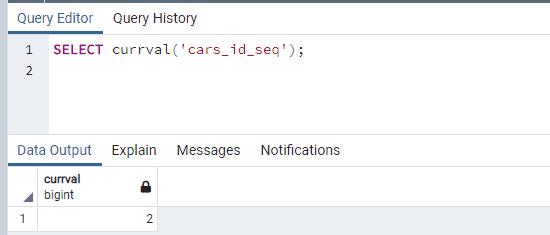
The above statement returns 2 as the current value of the sequence as the last id value is 2.
Multiple rows can be inserted into the table, in that case, it will keep on assigning the next value of the sequence to the id column sequentially.
INSERT INTO CARS(brand)
VALUES
('Hyundai'),
('Jeep'),
('Tesla');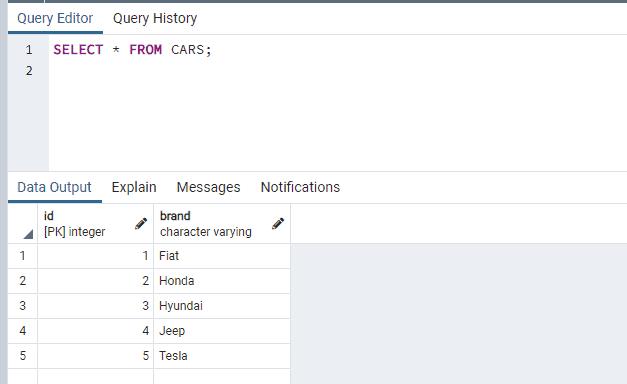
Thus, you can use sequence as the SERIAL type with the table.
