PostgreSQL: Self Join
The self join is a join that joins a table to itself. The self join is mainly used to query hierarchical data or compare rows of a table.
In self join, the same table is used twice with different table aliases. The INNER JOIN, LEFT JOIN or RIGHT JOIN can be used to perform Self join.
SELECT <table_1.column_name(s)>, <table_1.column_name(s)>
FROM <table_1>
INNER JOIN <table_1>
ON <table_1.column_name> = <table_1.column_name>;For the demo purpose, we will use the following Employee table.
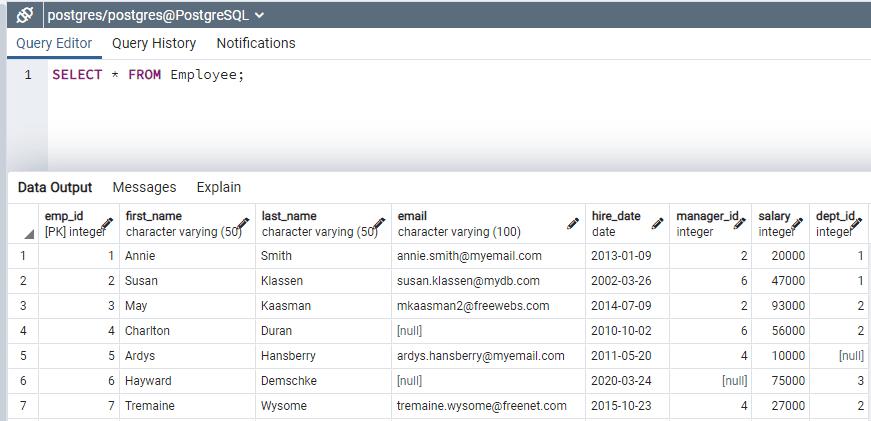
In the above Employee table, the manager_id column references to emp_id column. The employee has manager assigned and manager will be an employee. The value in manager_id column shows the manager that the employee directly reports to. When manager_id column is null for any employee that means that the employee does not report to anyone, that employee might be a top manager.
The following query shows hierarchical data of manager and employee.
SELECT
emp.emp_id employee_id,
emp.first_name || ' ' || emp.last_name employee,
mgr.emp_id manager_id,
mgr.first_name || ' ' || mgr.last_name manager
FROM employee emp INNER JOIN employee mgr
ON emp.manager_id = mgr.emp_id
ORDER BY manager;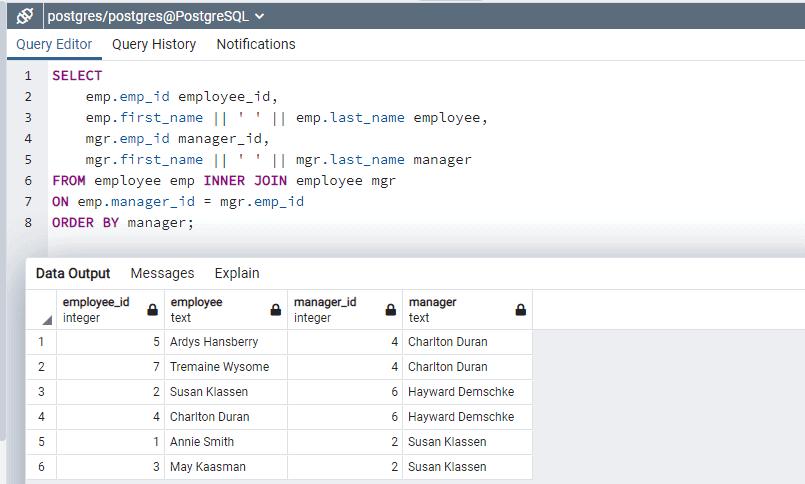
The above query references the Employee table twice once as Employee and the other as the Manager and uses INNER JOIN. We have given table alias as emp for Employee and mgr for the manager.
An Employee with emp_id 5 and 7 have manager as 4, employees with emp_id 1 and 3 have manager as 2. Employee with emp_id 2 and 4 reports to employee id 6. Notice that employee id 6 does not have any manager assigned, he is at the top level and not shown as a row in the above query result. To show top-level employee also, use LEFT JOIN.
SELECT
emp.emp_id employee_id,
emp.first_name || ' ' || emp.last_name employee,
mgr.emp_id manager_id,
mgr.first_name || ' ' || mgr.last_name manager
FROM employee emp LEFT JOIN employee mgr
ON emp.manager_id = mgr.emp_id
ORDER BY manager;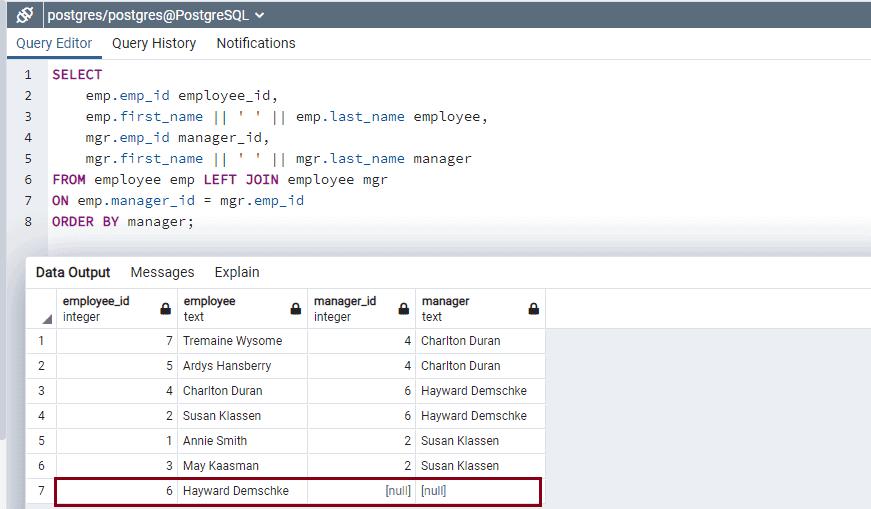
Self join can be used to compare data of the same table. Let's compare data of Employee table with itself and list employees that belong to same department.
SELECT
emp1.first_name || ' ' || emp1.last_name employee,
emp2.first_name || ' ' || emp2.last_name employee,
emp1.dept_id department
FROM employee emp1 INNER JOIN employee emp2
ON emp1.emp_id <> emp2.emp_id
AND emp1.dept_id = emp2.dept_id;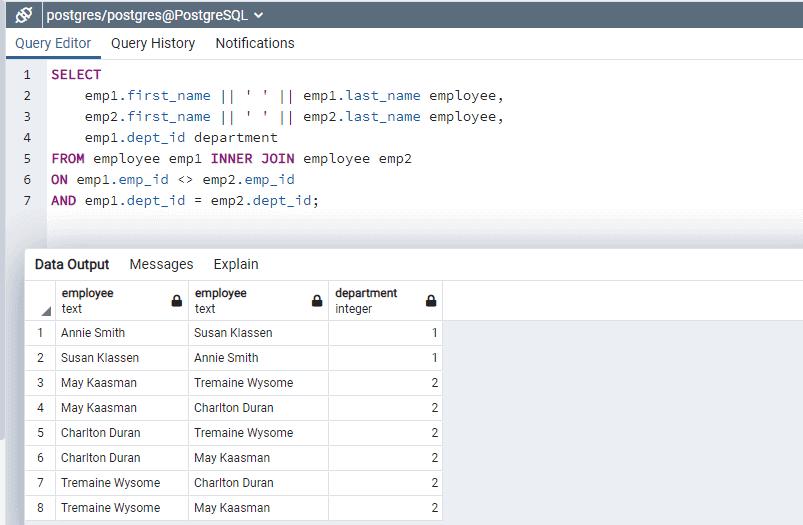
In the above query, we took the INNER JOIN of employee table with itself. We used emp1.emp_id <> emp2.emp_id to join tables and emp1.dept_id = emp2.dept_id to compare the dept_id of employees.
