C# - ArrayList
In C#, the ArrayList is a non-generic collection of objects whose size increases dynamically. It is the same as Array except that its size increases dynamically.
An ArrayList can be used to add unknown data where you don't know the types and the size of the data.
Create an ArrayList
The ArrayList class included in the System.Collections namespace. Create an object of the ArrayList using the new keyword.
using System.Collections;
ArrayList arlist = new ArrayList();
// or
var arlist = new ArrayList(); // recommendedAdding Elements in ArrayList
Use the Add() method or object initializer syntax to add elements in an ArrayList.
An ArrayList can contain multiple null and duplicate values.
// adding elements using ArrayList.Add() method
var arlist1 = new ArrayList();
arlist1.Add(1);
arlist1.Add("Bill");
arlist1.Add(" ");
arlist1.Add(true);
arlist1.Add(4.5);
arlist1.Add(null);
// adding elements using object initializer syntax
var arlist2 = new ArrayList()
{
2, "Steve", " ", true, 4.5, null
};Use the AddRange(ICollection c) method to add an entire Array, HashTable, SortedList, ArrayList, BitArray, Queue, and Stack in the ArrayList.
var arlist1 = new ArrayList();
var arlist2 = new ArrayList()
{
1, "Bill", " ", true, 4.5, null
};
int[] arr = { 100, 200, 300, 400 };
Queue myQ = new Queue();
myQ.Enqueue("Hello");
myQ.Enqueue("World!");
arlist1.AddRange(arlist2); //adding arraylist in arraylist
arlist1.AddRange(arr); //adding array in arraylist
arlist1.AddRange(myQ); //adding Queue in arraylistAccessing an ArrayList
The ArrayList class implements the IList interface. So, elements can be accessed using indexer, in the same way as an array. Index starts from zero and increases by one for each subsequent element.
An explicit casting to the appropriate types is required, or use the var variable.
var arlist = new ArrayList()
{
1,
"Bill",
300,
4.5f
};
//Access individual item using indexer
int firstElement = (int) arlist[0]; //returns 1
string secondElement = (string) arlist[1]; //returns "Bill"
//int secondElement = (int) arlist[1]; //Error: cannot cover string to int
//using var keyword without explicit casting
var firstElement = arlist[0]; //returns 1
var secondElement = arlist[1]; //returns "Bill"
//var fifthElement = arlist[5]; //Error: Index out of range
//update elements
arlist[0] = "Steve";
arlist[1] = 100;
//arlist[5] = 500; //Error: Index out of rangeIterate an ArrayList
The ArrayList implements the ICollection interface that supports iteration of the collection types. So, use the foreach and the for loop to iterate an ArrayList. The Count property of an ArrayList returns the total number of elements in an ArrayList.
ArrayList arlist = new ArrayList()
{
1,
"Bill",
300,
4.5F
};
foreach (var item in arlist)
Console.Write(item + ", "); //output: 1, Bill, 300, 4.5,
for(int i = 0 ; i < arlist.Count; i++)
Console.Write(arlist[i] + ", "); //output: 1, Bill, 300, 4.5,Insert Elements in ArrayList
Use the Insert() method to insert an element at the specified index into an ArrayList.
Signature: void Insert(int index, Object value)
ArrayList arlist = new ArrayList()
{
1,
"Bill",
300,
4.5f
};
arlist.Insert(1, "Second Item");
foreach (var val in arlist)
Console.WriteLine(val);Use the InsertRange() method to insert a collection in an ArrayList at the specfied index.
Signature: Void InsertRange(int index, ICollection c)
ArrayList arlist1 = new ArrayList()
{
100, 200, 600
};
ArrayList arlist2 = new ArrayList()
{
300, 400, 500
};
arlist1.InsertRange(2, arlist2);
foreach(var item in arlist1)
Console.Write(item + ", "); //output: 100, 200, 300, 400, 500, 600,Remove Elements from ArrayList
Use the Remove(), RemoveAt(), or RemoveRange methods to remove elements from an ArrayList.
ArrayList arList = new ArrayList()
{
1,
null,
"Bill",
300,
" ",
4.5f,
300,
};
arList.Remove(null); //Removes first occurance of null
arList.RemoveAt(4); //Removes element at index 4
arList.RemoveRange(0, 2);//Removes two elements starting from 1st item (0 index)Check Element in ArrayList
Use the Contains() method to determine whether the specified element exists in the ArrayList or not. It returns true if exists otherwise returns false.
ArrayList arList = new ArrayList()
{
1,
"Bill",
300,
4.5f,
300
};
Console.WriteLine(arList.Contains(300)); // true
Console.WriteLine(arList.Contains("Bill")); // true
Console.WriteLine(arList.Contains(10)); // false
Console.WriteLine(arList.Contains("Steve")); // falseArrayList class due to performance issue. Instead, use List<object> to store heterogeneous objects. To store data of same data type, use Generic List<T>.ArrayList Class
The following diagram illustrates the ArrayList class.
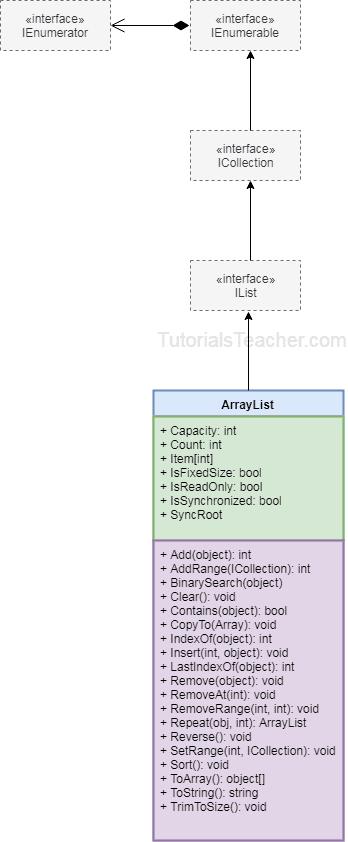
ArrayList Properties
| Properties | Description |
|---|---|
| Capacity | Gets or sets the number of elements that the ArrayList can contain. |
| Count | Gets the number of elements actually contained in the ArrayList. |
| IsFixedSize | Gets a value indicating whether the ArrayList has a fixed size. |
| IsReadOnly | Gets a value indicating whether the ArrayList is read-only. |
| Item | Gets or sets the element at the specified index. |
ArrayList Methods
| Methods | Description |
|---|---|
| Add()/AddRange() | Add() method adds single elements at the end of ArrayList. AddRange() method adds all the elements from the specified collection into ArrayList. |
| Insert()/InsertRange() | Insert() method insert a single elements at the specified index in ArrayList. InsertRange() method insert all the elements of the specified collection starting from specified index in ArrayList. |
| Remove()/RemoveRange() | Remove() method removes the specified element from the ArrayList. RemoveRange() method removes a range of elements from the ArrayList. |
| RemoveAt() | Removes the element at the specified index from the ArrayList. |
| Sort() | Sorts entire elements of the ArrayList. |
| Reverse() | Reverses the order of the elements in the entire ArrayList. |
| Contains | Checks whether specified element exists in the ArrayList or not. Returns true if exists otherwise false. |
| Clear | Removes all the elements in ArrayList. |
| CopyTo | Copies all the elements or range of elements to compitible Array. |
| GetRange | Returns specified number of elements from specified index from ArrayList. |
| IndexOf | Search specified element and returns zero based index if found. Returns -1 if element not found. |
| ToArray | Returns compitible array from an ArrayList. |
- Difference between Array & ArrayList
- ArrayList's Methods & Properties
